Innovative Molecular Gastronomy Food Techniques
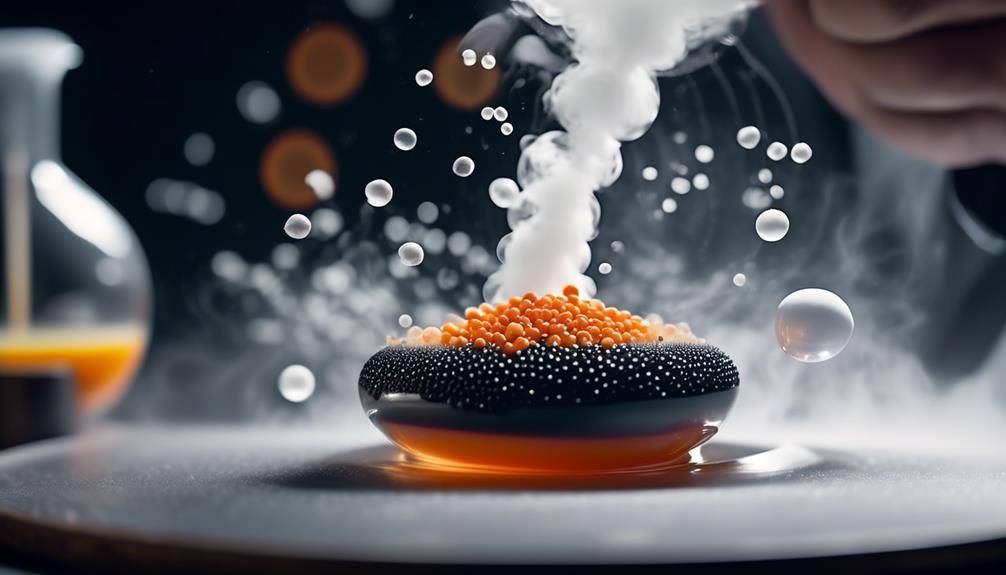

Molecular Gastronomy Food Techniques; Have you ever wondered how chefs create those beautiful, delicate foams that add an elegant touch to their dishes? Or how they transform liquids into gel-like textures that burst with flavor in your mouth? Welcome to the world of innovative molecular gastronomy food techniques. This fascinating field of culinary science has revolutionized the way we approach cooking, pushing the boundaries of traditional methods and introducing new and exciting ways to enhance our dining experiences.
From the art of spherification to the precision of sous vide, these techniques have captured the attention of chefs and food enthusiasts alike, and it’s not hard to see why. So, prepare to embark on a culinary journey where creativity knows no limits and flavors are elevated to new heights.
Foams and Gels
Foams and gels are commonly employed in molecular gastronomy to enhance the texture and presentation of dishes. These innovative techniques allow for the manipulation of flavors and textures, creating unique and visually appealing culinary experiences. Flavor pairing is one of the key aspects of molecular gastronomy, and foams and gels play a crucial role in this process.
Flavor pairing involves combining ingredients that complement each other, enhancing the overall taste of a dish. Foams and gels can be used to create concentrated flavors that complement the main components of a dish. By utilizing these techniques, chefs can achieve a harmonious balance of flavors, resulting in a more enjoyable dining experience.
Texture manipulation is another important aspect of molecular gastronomy, and foams and gels are excellent tools for achieving desired textures. Foams can be created by incorporating air into liquids, resulting in a light and airy texture. This can be used to add a delicate and smooth texture to dishes such as mousses or sauces. On the other hand, gels can provide a firmer and more solid texture. By using gelling agents such as agar-agar or gelatin, chefs can create textures ranging from soft and creamy to firm and jiggly.
Spherification
To further explore the realm of texture manipulation in molecular gastronomy, the next technique we will examine is known as spherification. Spherification is a culinary technique that involves creating small, spherical capsules of liquid that burst with flavor when consumed. It is a fascinating process that showcases the artistry of molecular gastronomy.
In spherification, flavor encapsulation is the key objective. The technique allows chefs to encapsulate various liquids, such as fruit juices, sauces, or even alcoholic beverages, within a thin gel membrane. This creates a unique dining experience as the liquid bursts in the mouth, releasing its flavorful content.
Spherification can be achieved through two different methods:
- Basic Spherification:
- In this method, a liquid is mixed with sodium alginate, a natural polysaccharide derived from seaweed.
- The mixture is then carefully dropped into a calcium-rich solution, which triggers the formation of a gel membrane around the liquid droplet.
- The resulting spheres can be enjoyed individually or incorporated into dishes for added visual appeal.
- Reverse Spherification:
- Reverse spherification follows a similar process, but with a twist.
- Instead of adding sodium alginate to the liquid, calcium ions are added to the liquid itself.
- The liquid is then dropped into a sodium alginate bath, causing the formation of a gel membrane around the liquid droplet.
Spherification showcases the innovative nature of molecular gastronomy, pushing the boundaries of culinary artistry. By encapsulating flavors in edible spheres, chefs can surprise and delight diners with bursts of taste. This technique adds a touch of whimsy and excitement to the dining experience, making it a favorite among gastronomy enthusiasts.
Sous Vide
Sous vide is a cooking method that involves sealing food in airtight bags and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath at a low and consistent temperature. This technique has gained popularity in recent years due to its ability to deliver precise and consistent results. The benefits of sous vide cooking techniques are numerous.
Firstly, sous vide allows for precise control over the cooking temperature, resulting in perfectly cooked food every time. By cooking food at a low and consistent temperature, sous vide ensures that the food is evenly cooked from edge to edge. This is especially beneficial when cooking delicate proteins, such as fish or eggs, which can easily overcook or become rubbery with traditional cooking methods.
Secondly, sous vide cooking techniques help to retain the natural flavors and nutrients of the food. Since the food is sealed in an airtight bag, it is cooked in its own juices, ensuring that the flavors are locked in. Additionally, the low cooking temperature helps to preserve the nutrients in the food, as they are not exposed to high heat for extended periods of time.
Furthermore, sous vide allows for precise timing and convenience. Once the food is sealed in the bag, it can be cooked for an extended period of time without the risk of overcooking. This makes it ideal for meal prepping or cooking in advance. Additionally, sous vide cooking techniques require minimal supervision, allowing you to focus on other tasks while your food cooks to perfection.
Emulsification
With the knowledge of precise control over temperature and the preservation of flavors and nutrients, the next technique to explore in molecular gastronomy is emulsification. Emulsification is a process that involves creating a stable mixture of two or more immiscible substances, such as oil and water, by dispersing one phase into another with the help of an emulsifying agent. This technique plays a crucial role in flavor pairing and texture manipulation, allowing chefs to create unique and innovative dishes.
Emulsification offers a wide range of possibilities in molecular gastronomy. Here are two key subtopics to consider:
- Emulsifying Agents:
- Emulsifying agents, also known as surfactants, are essential in stabilizing emulsions and preventing them from separating. Common emulsifying agents used in molecular gastronomy include lecithin, xanthan gum, and egg yolk. These agents work by reducing the surface tension between the two immiscible phases, allowing them to mix more easily.
- Lecithin, a natural emulsifier found in egg yolks and soybeans, is often used to create foams and airs. It helps in creating light and airy textures, adding a delicate touch to dishes.
- Techniques for Emulsification:
- High-speed blending: This technique involves using a high-powered blender to create stable emulsions quickly. By blending the oil and water together at high speeds, the droplets of one phase become dispersed throughout the other, resulting in a smooth and homogeneous mixture.
- Sous vide emulsions: Sous vide cooking allows for precise temperature control, which is crucial in creating stable emulsions. By vacuum sealing the ingredients and cooking them at a controlled temperature, emulsions can be created that have a perfectly balanced texture and flavor.
Emulsification is a powerful technique in molecular gastronomy that allows chefs to experiment with different flavors and textures. By understanding the role of emulsifying agents and employing various techniques, chefs can create visually stunning and innovative dishes that tantalize both the palate and the senses.
Nitrogen Cavitation
Nitrogen cavitation, a technique employed in molecular gastronomy, utilizes the power of nitrogen gas to create rapid pressure changes that result in unique textural transformations in food. This innovative method involves subjecting food to high pressure processing with nitrogen gas, leading to various effects such as flavor encapsulation.
The basic principle behind nitrogen cavitation is the application of high pressure using nitrogen gas. By rapidly pressurizing and depressurizing a food sample, the nitrogen gas creates tiny bubbles within the food matrix. These bubbles collapse under the sudden change in pressure, causing a cavitation effect. This process leads to physical and chemical changes within the food, resulting in new textures and flavors.
One of the key benefits of nitrogen cavitation is flavor encapsulation. The high-pressure environment allows flavors and aromas to penetrate deep into the food, enhancing the overall taste experience. The rapid pressure changes created by nitrogen cavitation also disrupt the food structure, leading to the formation of unique textures and mouthfeel.
Nitrogen cavitation is commonly used in the culinary world to create innovative dishes. For example, it can be employed to create foams, gels, and emulsions with unique textures and flavors. Additionally, this technique is often used to infuse flavors into ingredients, such as infusing fruits with the essence of herbs or spices.
Innovative Molecular Gastronomy Food Techniques; Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Create Different Flavors and Textures Using Foams and Gels in Molecular Gastronomy?
To create different flavors and textures using foams and gels in molecular gastronomy, you need to explore the science behind foam stability and gel formation. This allows for innovative techniques in molecular gastronomy.
What Are the Key Ingredients and Steps Involved in the Process of Spherification?
To achieve spherification, you need key ingredients like sodium alginate and calcium chloride, along with specific steps like creating a sodium alginate bath and dropping the liquid into it. This technique allows for different flavors and textures in molecular gastronomy.
Can You Explain the Benefits of Using Sous Vide Cooking Technique in Molecular Gastronomy?
The benefits of using sous vide cooking technique in molecular gastronomy include precise temperature control, which allows for consistent and even cooking. This is crucial in achieving the desired textures and flavors in innovative culinary creations.
What Are Some Popular Emulsification Techniques Used by Chefs in Molecular Gastronomy?
Some popular emulsification techniques used by chefs in molecular gastronomy include reverse spherification, air foams, and lecithin-based emulsions. These techniques allow for avant garde presentations and create unique textures and flavors in dishes.
How Does Nitrogen Cavitation Work and What Are Its Applications in Molecular Gastronomy?
Nitrogen cavitation is a technique used in molecular gastronomy. It involves subjecting food to high-pressure nitrogen gas, causing bubbles to form and rapidly collapse. This process can be used to create unique textures and flavors in dishes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the implementation of innovative molecular gastronomy techniques such as foams and gels, spherification, sous vide, emulsification, and nitrogen cavitation has revolutionized the culinary world. These techniques have allowed chefs to create unique textures, flavors, and presentations in their dishes. By harnessing the principles of chemistry and physics, molecular gastronomy has elevated the art of cooking to new heights, providing an exciting and immersive dining experience for food enthusiasts.